Each Step in the process of forming sediment. We can differentiate between sedimentary rock from Metamorphic rock on bedding and foliation.
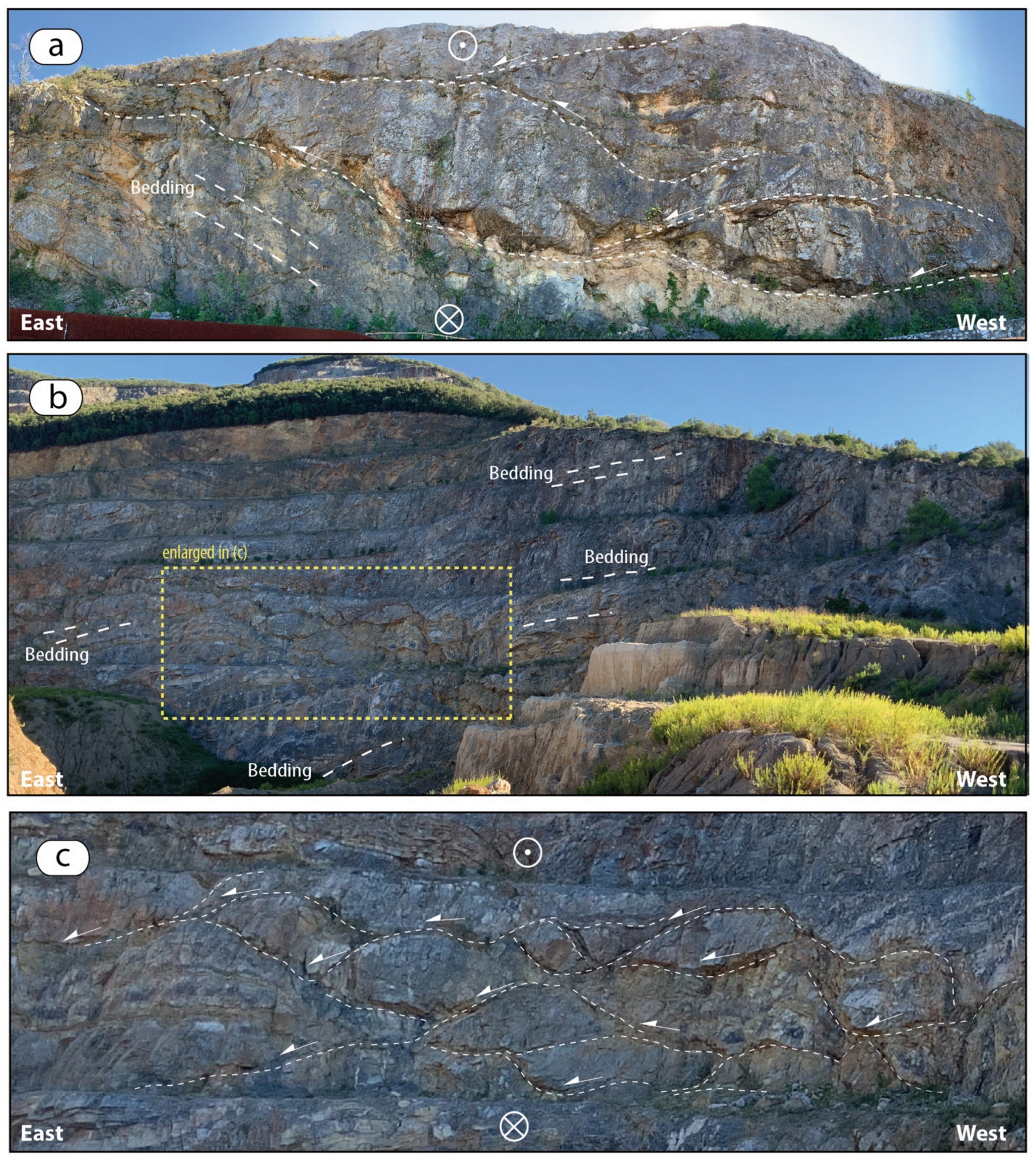
Geosciences Free Full Text The Gavorrano Monzogranite Northern Apennines An Updated Review Of Host Rock Protoliths Thermal Metamorphism And Tectonic Setting Html
Includes the Knife Lake Group and the Lake Vermilion Formation in northeastern Minnesota.

Are bedding in sedimentary rock conteibute mineralisation of tin. An ancient river channel Cross bedding Direction force depositing nature current composition texture of sand source rock in erosional env fossilised tree trunk indicate env of equilibrium ENVIRONMENTS CLASSIFIED Classification of sedimentary rocks in to various groups and sub groups Based on detailed analysis of sedimentary environments ENVIRONMENTS CLASSIFIED This classification. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering for example in the construction of roads houses tunnels canals or other. Sedimentary deposits of iron oxides and hydrous aluminum oxide are of this type.
Williams 1982 recognised two Proterozoic folding events and two further episode in the Mid Devonian to Early. In that case sedimentary rocks are derived rocks because they are formed from fragments of pre-existing rocks. The only family of rock in which natural gas petroleum coal uranium and salt form and from which these are extracted in abundance.
Ore minerals in skarns may be associated with calc-silicate minerals such as epidote tremolite zoisite wollastonite Silica iron and magnesium are supplied by hydrothermal fluids that evolve from the magma late in the cooling history. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata forming a structure called bedding. Sedimentary Rocks Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Soils Sedimentary Rocks Processes of the rock cycle Weathering Soils Erosion Transportation Deposition sedimentation Burial Diagenesis Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering.
Sometimes the bedding contacts are favorable places for skarns to form. Bedding is sedimentary process of rock formation while foliation is Metamorphic rock process. These can carry sediment small particals from one place to another place with a particular sequence.
Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features in sediments and sedimentary rocks formed at the time of deposition. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Rivers oceans winds and rain runoff all have the ability to carry the particles washed off of eroding rocks.
The rock its strength density sound velocity permeability or ability for water to flow through the pores and other attributes. These beds range from millimeters to centimeters thick and can even go to meters or multiple meters thick. The most common position for tin-tantalum mineralisation to occur is in the pegmatite wall zone.
Formation of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are the product of 1 weathering of preexisting rocks 2 transport of the weathering products 3 deposition of the material followed by 4 compaction and 5 cementation of the sediment to form a rock. Sedimentary structures are the larger generally three-dimensional physical features of sedimentary rocks. They are formed from sedimentary rocks being deposited on the Earths solid surface over long periods of time.
Layers of beds are called strata. To bedding of the host rock. Metasedimentary rocks undivided - Graywacke slate local units of conglomerate arenite graphitic slate fine-grained felsic volcanogenic and volcaniclastic rocks lean oxide iron-formation and its metamorphic equivalents.
Such material called detritus consists of fragments of rocks and mineralsWhen the energy of the transporting current is not strong enough to carry these particles the particles drop out in the process of sedimentation. Skarn is a relatively simple rock type formed when a magma body intrudes into carbonate sedimentary rocks such as limestone or dolomite. An exploration target copper estimate of 971000t at 15 Cu has also been reported with tungsten silver and gold known to occur in association with similar tin and copper mineralisation.
In other cases the ore deposits or more precisely ore minerals may be present in an enclosing rock called the country rock or the host rock. Bedding planes Joints and faults. Deposition of the sediment.
The most important geological processes that lead to the creation of sedimentary rocks are erosion weathering dissolution. At the contact between the two rock types a collection of course-grained calc-silicate minerals mostly the minerals garnet and pyroxene form as a result of the heat and fluids released by the cooling magma. A current published non JORC resource of 400000t at 04 tin open cut and 737000t at 138 tin underground.
The bulk of the tin mineralisation in the Mount Bischoff Inlier is hosted by sedimentary rocks at the top of the preserved Neoproterozoic sequence which has a complex structural history but are of very low metamorphic grade. Just as important to rock breakage using explosives are the large-scale or field-scale properties of rock. Dating of tantalite cassiterite U-Pb SIMS and greisen-associated muscovite Ar-Ar in pegmatites of the Bynoe pegmatite field indicates a mineralisation age of 17401720 Ma.
The only family of rock containing an abundant record of life forms and the changes of life forms throughout geologic time. Sedimentary structures include features like bedding ripple marks fossil tracks and trails and mud cracks. Water and air are responsible for bedding.
Sediments and sedimentary rocks are characterized by bedding which occurs when layers of sediment with different particle sizes are deposited on top of each other. Sedimentary rocks are formed on or near the Earths surface in contrast to metamorphic and igneous rocks which are formed deep within the Earth. In the Bynoe pegmatite field ore minerals occur in two generations.
Weathering Breaks pre-existing rock into small fragments or new minerals. Significance of sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rock - Sedimentary rock - Sedimentary structures.
They are best seen in outcrop or in large hand specimens rather than through a microscope. In such cases the host rock itself is removed in the first stage of mining. The strata are layered in the same order that they were deposited permitting discrimination as to which beds are.
These include the rocks. Beds are the layers of sedimentary rocks that are distinctly different from overlying and underlying subsequent beds of different sedimentary rocks. Transportation of the sediments to a sedimentary basin.
Burial and Lithification to make sedimentary rock.

Typical Sedimentary Features Of The Ulveryggen Dypelva And Stangvatnet Download Scientific Diagram
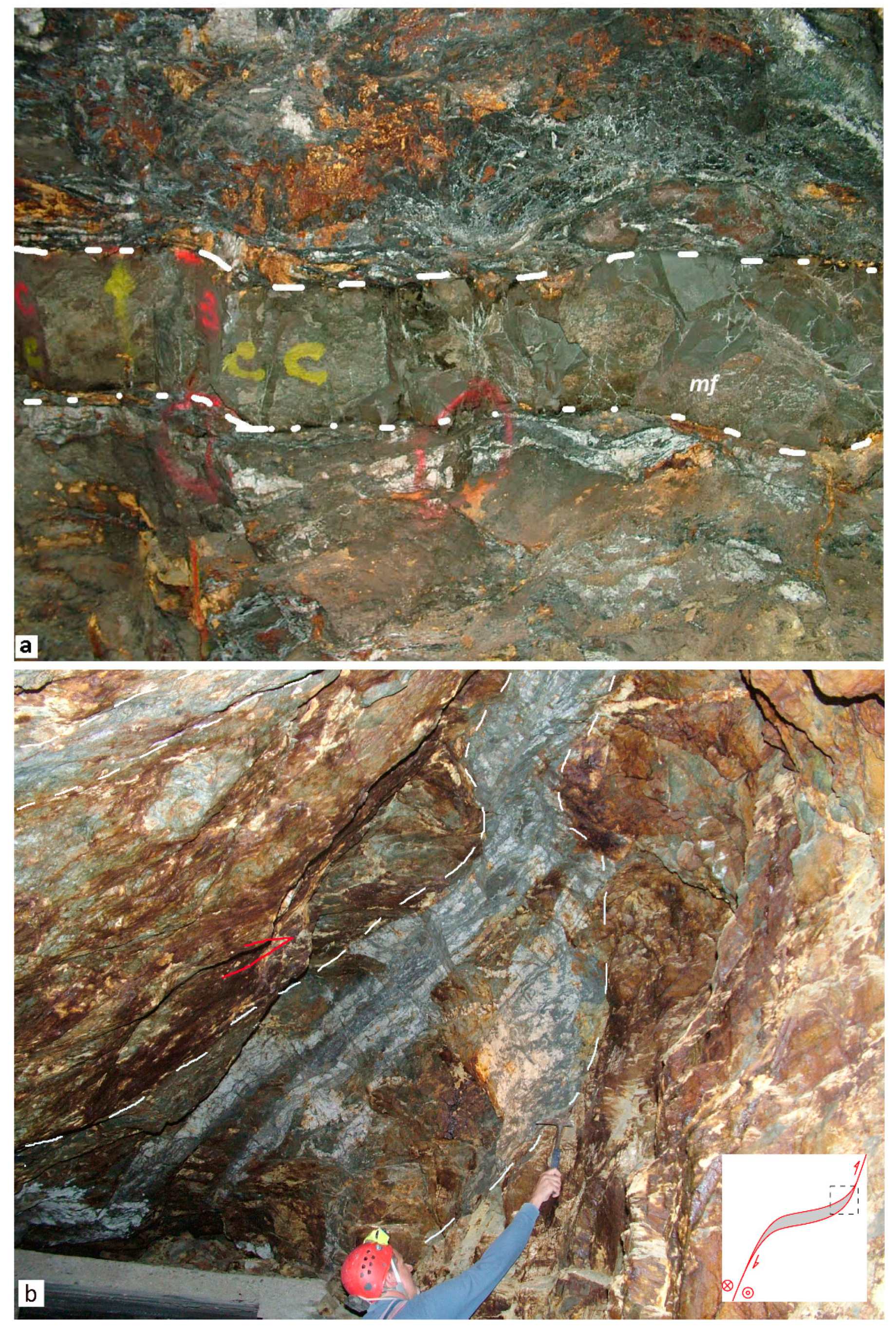
Minerals Free Full Text Structural Controls Of Ore Mineralization In A Polydeformed Basement Field Examples From The Variscan Baccu Locci Shear Zone Se Sardinia Italy Html

Photographs Illustrating The Cassiterite Rich Stringer System Of Corvo Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Geology Of The Cassiterite Mineralisation In The Rutongo Area Rwanda Central Africa Current State Of Knowledge

Minerals Free Full Text Linking Gold Systems To The Crust Mantle Evolution Of Archean Crust In Central Brazil Html
Tidak ada komentar